| Attribute |
Details |
Attribute |
Details |
| Sample |
Support |
Type |
Wire |
| Shape |
Straight Wires,
Coils, Spools |
Processing Service |
Bending, Welding, Decoiling,
Cutting, Punching |
Surface
Treatment |
Polishing, Rolled,
Sand Blasted Surface |
End Treatment |
Polished, Cutted |
| Application |
Medical, Industry |
Marking Method |
Electrocorrosion |
| Condition |
Annealed, Cold Rolled
Hot Rolled |
Transport Package |
Export Packing |
| Specification |
Customized |
Trademark |
HUONA |
| Origin |
China |
HS Code |
8108902000 |
Production
Capacity |
2000 Tons/Year |
|
|
Titanium Wire Description:Titanium wires are made through multiple drawing processes, we have a variety of titanium and titanium alloy titanium wires,
including 0.20-0.28 titanium wires for surgical staplers, 0.8-4.0 straight wires for orthopedics and dentistry,
industrial titanium welding wires and other series of wires.
Titanium Wire Specifications
| Grade |
Gr1,Gr2,Gr3,Gr4,Gr5(Ti-6Al-4V),Gr9(Ti-3Al-2.5V),Gr23(Ti-6Al-4V ELI),etc |
| Standard |
ASTM F67;ASTM F136; ISO5832-2;ISO5832-3;AMS4928;AMS4963;AMS4965;AMS4967;ASTM B348; ASTM B863 |
| Diameter(mm) |
0.1~4.75mm |
| Shape |
Straight, Coils, Spools |
| Condition |
Annealed (M), Cold rolled(Y), Hot rolled(R) |
| Surface |
Bright Surface |
Titanium Wire Features:High Surface Finish
Good Roundness
Small Tolerances
High Dimensional Consistency
Stable Performance
Uniform Composition
Fine Grain Organization
Excellent Overall Performance
Long Fatigue Life
Applications of Titanium Wires
1. Medical: Used in surgical implants like bone screws, dental wires, and cardiovascular stents due to its biocompatibility
and resistance to bodily fluids.
2. Aerospace: Essential for aircraft components such as fasteners, springs, and electrical connectors due to
its high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to corrosion.
3. Chemical Processing: Employed equipment for handling corrosive chemicals and acids, such as valves, fittings,
and mesh screens, due to their corrosion resistance.
4. Electronics: Utilized in electronic devices for wire bonding, connectors, and antennas due to its conductivity and resistance to corrosion.
5. Jewelry: Found in high-end jewelry for its hypoallergenic properties, durability, and ability to be colored through anodizing.
6. Art and Design: Used by artists and designers for sculptural works and architectural installations due to its malleability and aesthetic appeal.
7. Automotive: Employed in automotive applications such as exhaust systems, springs, and suspension components
for their lightweight and high strength.
8. Sports and Recreation: Utilized in sports equipment such as bicycle frames, fishing rods, and golf club shafts for
its lightweight and durable properties.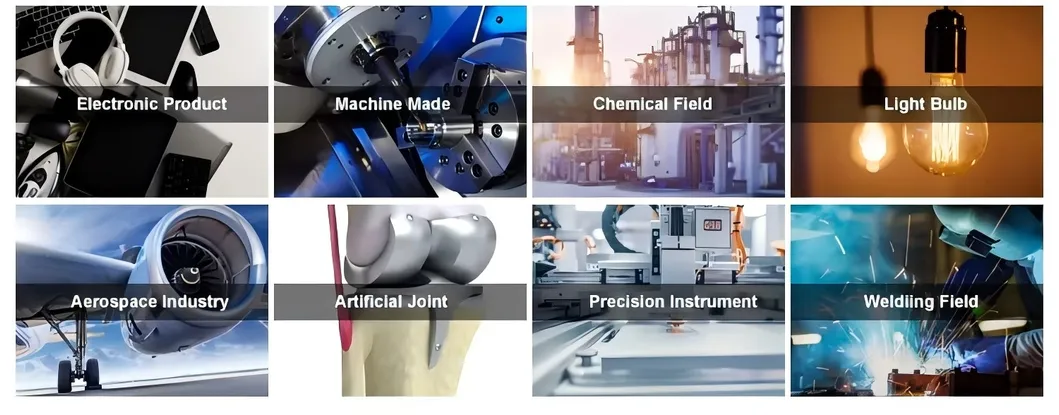 Chemical Composition
Chemical Composition
ASTM B863 Chemical Requirements:
| Grade |
UNS NO. |
Composition, % |
| Carbon, max |
Oxygen, max |
Nitrogen, max |
Hydrogen, B, C max |
Iron, max |
Aluminum |
Vanadium |
Palladium |
Ruthenium |
Nickel |
Molybdenum |
Chromium |
Cobalt |
Zirconium |
Niobium |
Tin |
Silicon |
Other Elements,,max.each |
Other Elements,max total |
Titanium G |
| 1 |
UNS R50250 |
0.08 |
0.18 |
0.03 |
0.015 |
0.20 |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
|
... |
0.1 |
0.4 |
balance |
| 2 |
UNS R50400 |
0.08 |
0.25 |
0.03 |
0.015 |
0.30 |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
|
... |
0.1 |
0.4 |
balance |
| 3 |
UNS R50550 |
0.08 |
0.35 |
0.05 |
0.015 |
0.30 |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
|
... |
0.1 |
0.4 |
balance |
| 4 |
UNS R50700 |
0.08 |
0.40 |
0.05 |
0.015 |
0.50 |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
|
... |
0.1 |
0.4 |
balance |
| 5 |
UNS R56400 |
0.08 |
0.20 |
0.05 |
0.015 |
0.40 |
5.5-6.75 |
3.5-4.5 |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
|
... |
0.1 |
0.4 |
balance |
| 9 |
UNS R56320 |
0.08 |
0.15 |
0.03 |
0.015 |
0.25 |
2.5-3.5 |
2.0-3.0 |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
|
... |
0.1 |
0.4 |
balance |
| 23 |
UNS R56407 |
0.08 |
0.13 |
0.03 |
0.0125 |
0.25 |
5.5-6.5 |
3.5-4.5 |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
|
|
0.1 |
0.4 |
balance |
Analysis Tolerances
ASTM B863 Analysis Tolerances:
| Element |
Product Analysis Limits, max or Range, % |
Permissible Variation in Product Analysis |
| Aluminum |
0.5 to 2.5 |
±0.20 |
| Aluminum |
2.5 to 6.75 |
±0.40 |
| Carbon |
0.10 |
+0.02 |
| Chromium |
0.1 to 0.2 |
±0.02 |
| Chromium |
5.5 to 6.5 |
±0.30 |
| Hydrogen |
0.02 |
+0.002 |
| Iron |
0.80 |
+0.15 |
| Iron |
1.2 to 1.8 |
±0.20 |
| Molybdenum |
0.2 to 0.4 |
±0.03 |
| Molybdenum |
0.6 to 1.2 |
±0.15 |
| Molybdenum |
1.5 to 4.5 |
±0.20 |
| Molybdenum |
14.0 to 16.0 |
±0.50 |
| Nickel |
0.3 to 0.9 |
±0.05 |
| Niobium |
2.2 to 3.2 |
±0.15 |
| Niobium |
>30 |
±0.50 |
| Nitrogen |
0.05 |
+0.02 |
| Oxygen |
0.30 |
+0.03 |
| Oxygen |
0.31 to 0.40 |
±0.04 |
| Palladium |
0.01 to 0.02 |
±0.002 |
| Palladium |
0.04 to 0.08 |
±0.005 |
| Palladium |
0.12 to 0.25 |
±0.02 |
| Ruthenium |
0.02 to 0.04 |
±0.005 |
| Ruthenium |
0.04 to 0.06 |
±0.005 |
| Ruthenium |
0.08 to 0.14 |
±0.01 |
| Silicon |
0.06 to 0.50 |
±0.02 |
| Tin |
0.6 to 3.0 |
±0.15 |
| Vanadium |
0.6 to 4.5 |
±0.15 |
| Vanadium |
7.5 to 8.5 |
±0.40 |
| Zirconium |
0.6 to 1.4 |
±0.15 |
| Zirconium |
3.5 to 4.5 |
±0.20 |
| Residuals(each) |
0.15 |
+0.02 |
Mechanical Properties
ASTM B863 Tensile Requirements:
| Grade |
Tensile Strength, min |
Yield Strength (0.2 % Offset) min or range |
Elongation in 4D, min, % |
Reduction of Area, min % |
| KSI |
MPa |
KSI |
MPa |
| 1 |
35 |
240 |
20 |
138 |
20 |
24 |
| 2 |
50 |
345 |
40 |
275 |
18 |
20 |
| 3 |
65 |
450 |
55 |
380 |
18 |
18 |
| 4 |
80 |
550 |
70 |
483 |
15 |
15 |
| 5 |
130 |
895 |
120 |
828 |
10 |
10 |
| 9 |
90 |
620 |
70 |
483 |
15 |
15 |
| 23 |
115 |
793 |
110 |
759 |
10 |
10 |
Tolerances:
ASTM B863 Permissible Variations in Size for Titanium Wire
| Specified Diameter, in. (dimension if shape wire) |
Variations, in. |
| Wire as Coil or on Spools |
Cut Straight Lengths A |
| 0.010 to 0.045, incl |
±0.001 |
±0.0015 |
| Over 0.045 to 0.062, incl |
±0.0015 |
±0.002 |
| Over 0.062 to 0.090, incl |
±0.002 |
±0.0025 |
| Over 0.090 to 0.187, incl |
±0.003 |
±0.003 |
| Over 0.187 to 0.250 |
±0.004 |
±0.004 |
| Over 0.250 to 0.750 |
±0.005 |
±0.005 |
 Alfred***We received the goods, everything went fine. Perfect packaging, good product quality, good price - we are satisfied.
Alfred***We received the goods, everything went fine. Perfect packaging, good product quality, good price - we are satisfied. May***The product quality is very good, beyond my expectations, the actual use of fully meet my needs, we will buy again.
May***The product quality is very good, beyond my expectations, the actual use of fully meet my needs, we will buy again. Matthew***I bought low expansion alloy from Joy, She is a very responsible lady, Huona's products quality is pretty good.
Matthew***I bought low expansion alloy from Joy, She is a very responsible lady, Huona's products quality is pretty good.










